Types of Skin Cancer – Risk Factors
The rapid growth of cancer cells that begins in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) is called skin cancer. The main cause of skin cancer is the exposure of skin to harmful UV rays. UV rays harm the cells called melanocytes These help in the production of melanin, which forms a protective layer on the skin. The different types of skin cancer are associated with various risk factors. We can prevent the occurrence of skin cancer by taking some precautionary measures.
Some of the common risk factors associated with the different types of skin cancer are:
- Fair-skinned individuals
Due to the absence of adequate melanin in the skin, fair-skinned individuals are often prone to skin cancer. However, individuals with darker skin can also be affected due to frequent exposure to harmful UV rays in the sunlight.
- Medical history of sunburns
An individual having a childhood or teenage history of sunburns is more prone to skin cancer in adulthood. - Residing in high altitude places with sunny climate
Individuals who reside in sunny climate areas are frequently exposed to harmful UV rays in the sunlight. The sun radiation is stronger in higher elevated areas as it receives the strongest sunlight. - Frequent exposure to sunlight
People who spend more time under the sun without proper clothing or a protective layer of sunscreen are more prone to skin cancer. Skin cancer is also commonly diagnosed in individuals who use tanning beds and lamps. - Moles
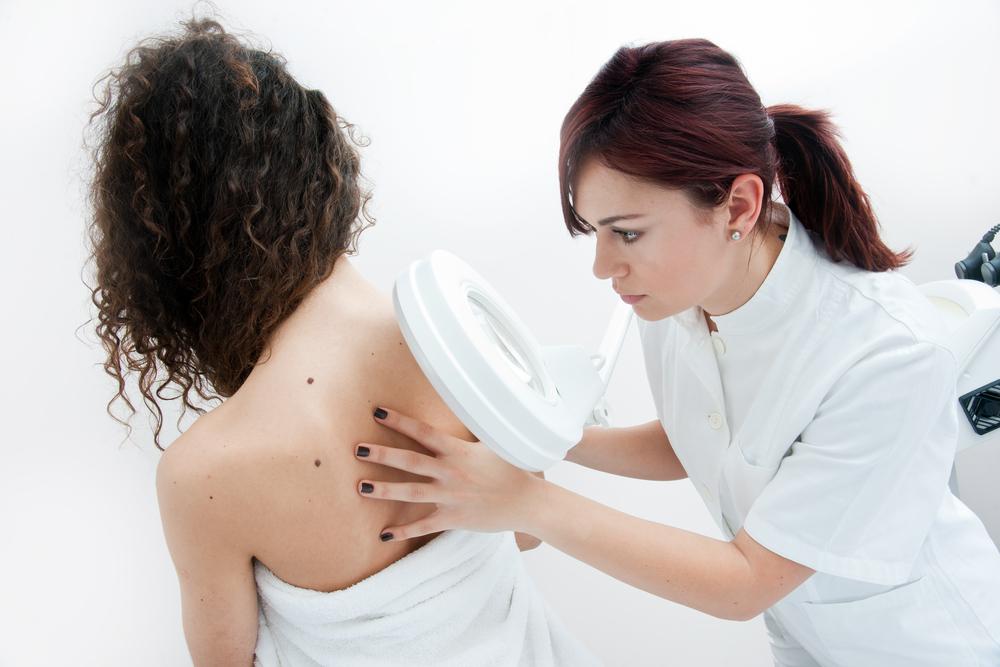
The appearance of dysplastic nevi or abnormal moles leads to skin cancer. These moles look different from normal moles as they are larger and have an irregular shape. A dermatologist should be consulted if you notice frequent changes in the appearance of the mole. - Personal history of skin cancer
If you have had a history of skin cancer in the past, you are more likely to get it again. - Weak immune system
Individuals with immune system problems such as HIV/ AIDS are at higher risk of developing skin cancer. This includes individuals with organ transplant taking immunosuppressant medications. - Untreated precancerous skin lesions
Individuals with untreated cancerous skin lesions are at a higher risk of being diagnosed with skin cancer. A dermatologist should be consulted if any cancerous lesions called actinic keratoses is found. They usually appear on body parts that are frequently exposed to sunlight such as arms, face, neck, and head. These lesions appear to be scaly and rough and their color varies from brown to dark pink. These types of lesions are often found in fair-skinned individuals. - Heredity
Skin cancer can also be caused due to a genetic disorder passed on from ancestors. If there is a family history of skin cancer, an individual is at an increased risk of getting skin cancer. - Frequent exposure to arsenic
Individuals who are frequently exposed to chemical substances such as arsenic are more prone to skin cancer. - Frequent exposure to radiation
Individuals who undergo radiation therapy to treat skin conditions such as acne and eczema are at a higher risk of skin cancer, especially basal cell carcinoma.